User Behavior Analytics takes center stage in the world of cybersecurity, offering a unique perspective on detecting threats and anomalies. Get ready to dive into a realm of data-driven security like never before.
In today’s digital landscape, understanding user behavior is crucial to safeguarding sensitive information and combating cybersecurity threats. User Behavior Analytics, often referred to as UBA, plays a pivotal role in identifying patterns, anomalies, and potential risks within organizational networks. By analyzing user activities, it provides valuable insights that traditional security measures might overlook, making it a powerful tool in the fight against cyber threats.
Overview of User Behavior Analytics
User Behavior Analytics (UBA) is a cybersecurity approach that focuses on monitoring and analyzing user activities within an organization’s network to identify potential security threats. By scrutinizing patterns of behavior, UBA can detect anomalies or suspicious activities that may indicate a security breach.
Significance of User Behavior Analytics in Cybersecurity
Implementing UBA is crucial in enhancing cybersecurity measures as it provides a proactive approach to threat detection. Traditional security measures typically rely on predefined rules and signatures to identify threats, whereas UBA leverages machine learning and algorithms to identify deviations from normal user behavior.
By continuously monitoring user activities, UBA can help organizations detect insider threats, compromised accounts, and other malicious activities that may go unnoticed by traditional security tools. This proactive approach allows for quicker response times and mitigation of potential security incidents.
Primary Objectives of Implementing User Behavior Analytics
- Identifying insider threats: UBA helps in detecting anomalous behavior that may indicate an employee or insider threat.
- Improving incident response: By quickly identifying potential security incidents, organizations can respond promptly to mitigate risks.
- Enhancing data protection: UBA assists in safeguarding sensitive data by monitoring user access and activities.
Differences from Traditional Security Measures
Unlike traditional security measures that rely on static rules and signatures, UBA focuses on dynamic analysis of user behavior. Traditional tools may miss subtle changes or new attack techniques, whereas UBA adapts to evolving threats by learning from user activities and detecting deviations from normal behavior.
Importance of User Behavior Analytics
User Behavior Analytics plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity measures by detecting insider threats and identifying anomalous behavior. This proactive approach allows organizations to mitigate risks and prevent potential security breaches.
Detecting Insider Threats
User Behavior Analytics helps in detecting insider threats by monitoring user activities, identifying deviations from normal behavior patterns, and flagging suspicious actions. By analyzing user interactions with sensitive data and systems, organizations can pinpoint potential insider threats before they cause harm.
Identifying Anomalous Behavior
User Behavior Analytics is instrumental in identifying anomalous behavior that may indicate a security threat. By establishing baseline behavior profiles for users and systems, organizations can quickly detect deviations and take immediate action to investigate and respond to potential security incidents.
Real-World Scenarios
– In a financial institution, User Behavior Analytics detected an employee accessing confidential customer information outside of regular working hours, leading to the prevention of a data breach.
– A healthcare organization utilized User Behavior Analytics to identify an employee attempting to exfiltrate patient records, allowing for prompt intervention and protection of sensitive data.
– A retail company leveraged User Behavior Analytics to uncover a pattern of abnormal login attempts from a compromised account, enabling the organization to strengthen authentication measures and prevent unauthorized access.
Components of User Behavior Analytics
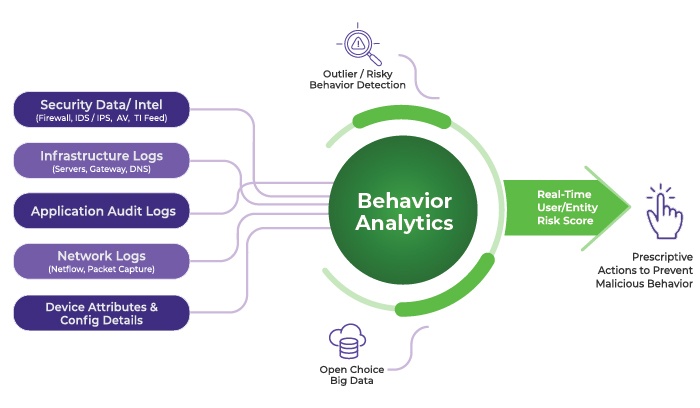
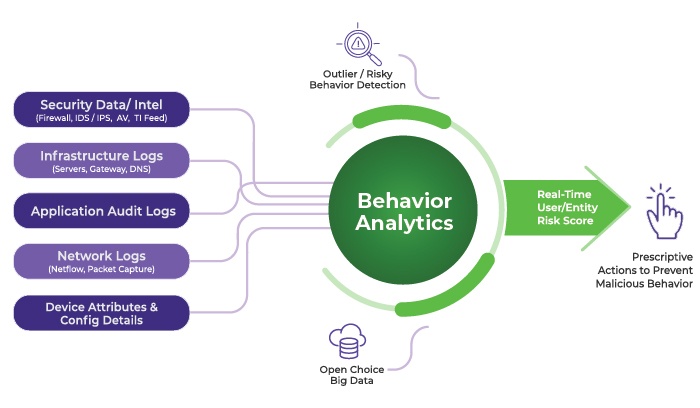
User Behavior Analytics systems consist of several key components that work together to analyze and interpret user actions and patterns. These components include data sources, algorithms, dashboards, and reports.
Data Sources Utilized in User Behavior Analytics
- Internal Data: Information collected from within the organization’s systems and applications, such as log files, databases, and application usage data.
- External Data: Data obtained from sources outside the organization, such as social media platforms, third-party applications, and public databases.
- Endpoint Data: Data generated by endpoint devices like computers, mobile devices, and IoT devices, providing insights into user interactions and behaviors.
Technology and Tools for Implementing User Behavior Analytics
- Machine Learning Algorithms: Utilized to detect anomalies, predict user behavior, and identify patterns within the data.
- Behavioral Biometrics: Tools that analyze unique user behavior traits like typing patterns, mouse movements, and navigation habits to enhance security.
- Visualization Tools: Dashboards and reports that present data in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format for decision-makers.
Challenges and Limitations of User Behavior Analytics
Deploying User Behavior Analytics can come with its fair share of challenges and limitations that organizations need to be aware of.
Common Challenges Faced when Deploying User Behavior Analytics
- Difficulty in defining normal user behavior patterns: One of the main challenges is establishing a baseline for what constitutes normal behavior, as this can vary greatly among different users and systems.
- High false positive rates: User Behavior Analytics tools may generate a large number of false alerts, leading to alert fatigue and potentially overlooking real threats.
- Data quality and integration: Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and integration of data from various sources can be a significant challenge in implementing User Behavior Analytics.
Limitations of User Behavior Analytics in Cybersecurity Contexts
- Inability to detect advanced threats: User Behavior Analytics may struggle to identify sophisticated and novel attack techniques that do not conform to known patterns of behavior.
- Lack of context: Understanding the context of user actions, such as changes in job roles or responsibilities, can be difficult for User Behavior Analytics tools, leading to misinterpretation of activities.
- Data privacy concerns: The collection and analysis of user data for behavior analytics raise privacy issues and regulatory compliance challenges that can limit the effectiveness of these tools.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges Associated with User Behavior Analytics
- Continuous monitoring and tuning: Regularly reviewing and refining the algorithms and thresholds used in User Behavior Analytics can help reduce false positives and improve accuracy.
- Collaboration across teams: Encouraging collaboration between security, IT, and business teams can provide additional context for user behavior analysis and enhance the effectiveness of the tools.
- Employee training and awareness: Educating employees about the purpose and benefits of User Behavior Analytics can help mitigate privacy concerns and ensure cooperation with monitoring efforts.
Best Practices for Implementing User Behavior Analytics
Implementing User Behavior Analytics can be a game-changer for organizations looking to enhance their cybersecurity measures and improve user experience. Here are some best practices to consider when deploying User Behavior Analytics systems:
Establish Clear Objectives
Before implementing User Behavior Analytics, organizations should clearly define their objectives and goals. Whether the focus is on detecting insider threats, improving user engagement, or enhancing security posture, having a clear vision will help guide the implementation process effectively.
Collect Relevant Data, User Behavior Analytics
It is crucial to collect relevant and high-quality data to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of User Behavior Analytics. Organizations should gather data from various sources, including network logs, application logs, and user activity logs, to provide a comprehensive view of user behavior.
Invest in Training and Education
Training employees on how to use User Behavior Analytics tools and interpret the results is essential for maximizing the system’s efficiency. Investing in training and education programs will empower users to leverage the full potential of User Behavior Analytics and make informed decisions based on the insights generated.
Regular Updates and Maintenance
To ensure the continued effectiveness of User Behavior Analytics, organizations should prioritize regular updates and maintenance. This includes updating algorithms, reviewing data sources, and fine-tuning the system to adapt to evolving threats and user behavior patterns.
Integrate with Existing Security Tools
Integrating User Behavior Analytics with existing security tools, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) solutions, can provide a more comprehensive view of the organization’s security posture. By combining different tools and technologies, organizations can strengthen their overall security strategy and improve threat detection capabilities.
Monitor and Evaluate Performance
Monitoring the performance of User Behavior Analytics systems is crucial to identifying any anomalies or potential issues. Regularly evaluating the system’s effectiveness and adjusting configurations based on feedback will help organizations optimize their user behavior monitoring capabilities.
Collaborate Across Departments
Effective implementation of User Behavior Analytics requires collaboration across different departments within an organization. By involving IT, security, compliance, and business teams in the deployment process, organizations can ensure a holistic approach to user behavior monitoring and analysis.